Growth Hacking Step-by-step
Welcome to the complete guide to growth hacking. In this guide, you will learn the fundamentals of growth hacking.
You will also learn the growth hacker’s mindset and all the frameworks you need to know to drive scalable growth.
Contents

What Is Growth Hacking?
You’ll come across many definitions of growth hacking – some more confusing than others.
While each of these statements can be said to be true about growth hacking, none of them actually define growth hacking completely.
The Definition of Growth Hacking
If you ask me the exact definition that covers all the key aspects of growth hacking, here’s what I have for you:
Finding implementations, often offbeat and creative hacks, to improve any given metric in the growth funnel using rapid experimentation, lean and agile principles, and scaling the execution based on data-driven decisions.
The growth hacking implementations in the above definition can refer to:
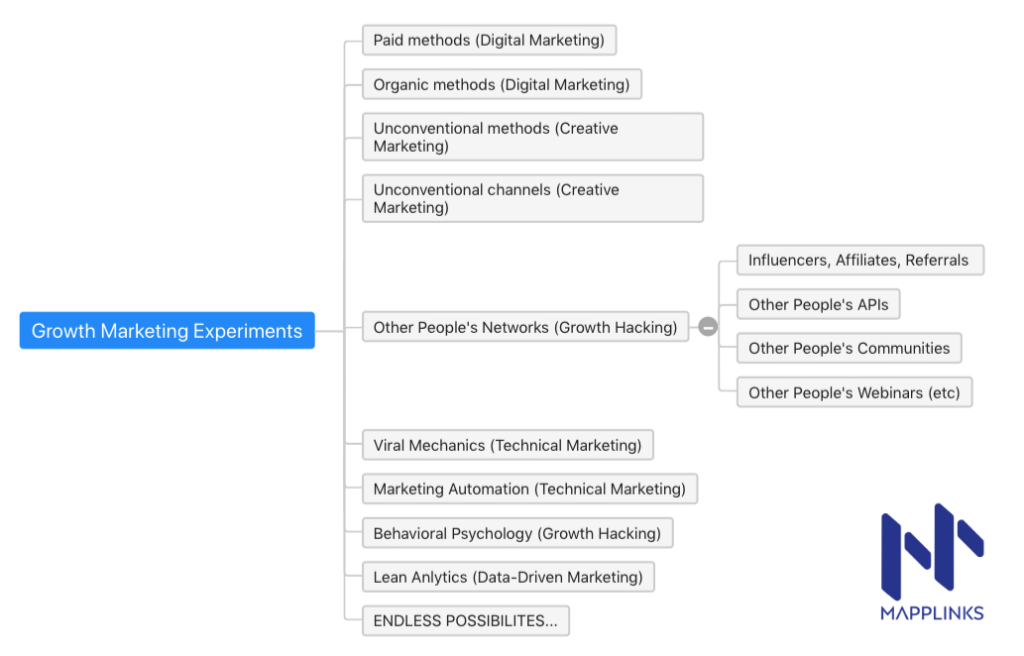
- Other People’s Networks
- Offbeat or unconventional channels
- Offbeat or unconventional methods
- Creative hacks implemented within the product
- Creative hacks implemented in the campaigns
All of these implementations are focused on a single metric in the A3R3 funnel which is the most useful growth funnel for selecting focus metrics is also known as the OMTM or the North Star.
Growth Hacking Metrics and Funnel
The A3R3 funnel or the AAARRR funnel is the one I use to select metrics for my growth hacking experiments as well as to understand the stage of the funnel, my users are in.
Here is the entire funnel visualized along with some examples of growth hacking metrics in each stage of the funnel:

All the growth hacks you will come across will focus on one of the metrics from the above growth funnel. Of course, multiple other growths metrics can improve as a result of focusing on one metric.
This is a great way to work on execution as small teams and startups can achieve results by staying super-focused on improving this single metric.
Growth Hackers like to call this metric the OMTM (one metric that matters) or the North Star metric.
Get the complete growth hacking dictionary and list of terms growth hackers use here.
Measures what matters: EXAMPLE OF NORTH STAR METRICS
Let’s take an example:
If your startup is an eCommerce company and you’ve recently set up your new store, your OMTM should probably be traffic. Once you a small amount of consistent traffic coming in, you can shift your focus on your Conversion Rate and work on CRO hacks for your eCommerce store.
Once your conversion rate is good, you can start focusing on your average ticket size.
So the focus metric will change over time for your startup and business and that is how it should be.
Other Examples of North Star Metrics
- SaaS startup Subscription
- Shopping Cart abandonment rate
- Average In-app Purchase size
- E-commerce Wishlist-to-cart conversion ratio
- Content Creation rate
- Social Media Engagement rate
- Ad Clickthrough rate
- Shopping Cart size
- App Installs-to-reviews ratio
- App Listing Conversion Rate
- SaaS startup Blog traffic to Free Trial Rate
- Landing page to Sign up Rate
- Cart to Checkout Conversion Rate
Build a Growth Hacker’s Mindset
You can pick the right metrics and understand what growth hacking is, but before you actually start executing the growth hacking process, you must think like a growth hacker.
The truth is: coming up with a few hacks will not make you a true growth hacker. Once you have the right mindset, you can find many growth hacks, hunt for tools to achieve results faster, discover cheaper alternatives for expensive marketing methods, and so on.
Some people already “Think Growth” while for others it will take some time to build the right mindset. The fastest way to achieve this mindset is to make it a part of your lifestyle.
The Growth Hacker’s mentality actually consists of multiple mindsets.
As a growth hacker, you must:


Use Offbeat Channels for Growth
The most common channels are usually expensive and saturated.
Digital marketers usually follow a playbook with the common & popular set of channels like Facebook, Linked In, Twitter, Instagram.
Rarely, social media campaigns are executed beyond this set while search campaigns run across the major advertising platforms like SM Ads and Google Ads.
As a growth hacker, you must think beyond the default digital or the traditional offline marketing channels to get better results, with less time and money.
Example #1
Airbnb “growth hacked” Craigslist. It was not a traditional marketing or Facebook Ads campaign.
Example #2
PayPal “growth hacked” eBay. It was not an Adwords or app advertising campaign.
Think outside the playbook of a digital marketer and follow the growth hacking process to make your creative ideas work.
More about the difference between a digital marketer and a growth hacker here.
That said, let’s get into the growth hacking process.
Learn the Process of Growth Experimentation
While growth hackers always say “Experiment, Experiment, Experiment”, a lot of them go into experimentation without a proper process in place.
To build your growth process, you must first have some fundamentals in place.

Prerequisites for Growth Hacking
Here are the fundamentals you need:
Minimum Viable Product
- If you’re an early-stage startup, make sure you’ve validated your audience with an MVP before you start growth experimentation.
User Personas
Answer the following questions about your users:
- What are the age group and gender of your audience?
- What is the target location of your users?
- What requirements do your users have?
- What problems do your users face?
- What is the lifestyle of your target audience?
- What roles are they currently in? (great for B2B)
Channel Personas
A channel persona is a definition of a channel that can be used for
your growth hacking experiments.
Some questions to ask to find your growth channels are:
- What kind of problem would the channel solve for a similar target
audience as mine - What are the other interests of my target audience?
- Where do people with similar interests hang out?
- Which tools or networks are review bloggers in my network writing
about? - What channels did my first users come from?
Once you have the fundamentals in place, you should start brainstorming growth hacking ideas for this startup or business-focused around your first North Star.
Growth Hacks and Ideas
Once you have the foundation of the process by documenting your pre-requisites, start by brainstorming ideas and growth hacks.
This is where the fun begins…
You will need to look at data, your competitors, and also your gut feeling to come up with excellent growth hacks:
WHERETO GET YOUR IDEAS FROM | HOW TO IMPROVE THE HACKS |
Past Data | Ideas from other campaigns, past data of experiments, both soft are hard data are useful here. |
Brainstorming | Data from putting multiple teams together in a room or online meeting to generate ideas |
Gut Feeling | Usually used more effectively for prioritizing ideas and improving upon them |
Competitor Analysis | See what growth hacks are working for your competitors or other startups with the same target audience as yours to generate more effective growth hacking ideas |
Make sure you have at least 10 ideas in the ideation phase so you can shortlist ideas later.
I usually start off with 8 ideas and I’ve repeated the growth hacking process for over 60 startups and businesses and always found the 1 big idea that scales from my set of 8. Sometimes, you can find the first idea to be the best fit for you but in most cases, you will have to experiment to get the gold!
Ice Framework for Prioritization
One of the biggest misconceptions about growth hacking is that it’s about finding a bunch of shortcuts and cool tricks.
Though there might be a small part of your growth hacking process, the main idea is to build repeatable and scalable processes to achieve growth.
A lot of blogs are written on growth hacking with negative perspectives while the authors don’t realize they’re talking about the
“shortcuts” and “tricks” and not really about the growth hacking process.
In fact, it’s sad that most people don’t really understand that growth hacking is a scalable process build of multiple frameworks.
One of the common frameworks we use as growth hackers is called the ICE framework and gives us an ICE score which helps prioritize the ideas and hacks we got in the last step.
HOW TO PRIORITIZE | IMPROVE THIS STAGE OF THE GROWTH |
Past Data | Ideas from other campaigns, past data of experiments, both soft are hard data are useful here. |
Top 3 Experiments | I stands for Impact, C stands for Confidence, and E stands for Ease. Sort your experiments by the ICE scores and |
Scoring Alternatives | Don’t shy away from using an alternative one or trying a different scoring method. |
What’s a good ICE score?
Remember, the ICE Score is for prioritization and usually not for elimination. So don’t think if you’ve got a good or a bad ICE score.

Execute the Experiment Tests
The next step is where the hustle comes in.
Here are some key points to remember for growth hacking execution:
EXECUTION GUIDE | HOW TO IMPROVE EXECUTION |
Duration | Design experiments that can be tested within |
Metrics | In some cases, improvement in one of the three metrics can make the test successful rather than one. |
Bias | (Yes, this is not what most growth hackers will tell you but it’s the truth) Avoid any personal bias creeps from the growth team. |
Analytics for Growth Hacking
Analytics is a part of every step of the growth hacking process as we’ve seen above.
A few key things to remember about Analytics are:

Useful Growth Hacking Terms
Here are some terms that you’ll hear quite often and they’ll be useful if you’re working with or as growth hackers:
Product Market Fit: Foundation of growth. When offerings and the audience is in sync.
One Metric That Matters (OMTM) or North Star Metric: One goal defined by a single metric which the entire startup should be working towards.
Growth Experiment: A potential growth hack, currently in the experiment stage.
Growth Hack: A growth experiment that is able to achieve the required OMTM.
Scalable Growth Hack: A growth hack with a YES output from the ESS which can also be automated using tech (bots, scripts, etc).
Unicorn Growth Hack: Exceptionally successful hacks (Not to be confused with the financial unicorn).
User Personas: Detailed definitions of how your target audience looks.
Channel Personas: Detailed definition of how your target channels look.
Funnel: A tool that helps you visualize the buyer’s journey or the path a prospect takes as they become familiar with your product, from introduction to conversion and beyond.
A3R3 Funnel: The growth hacking funnel I use and train on (A modification of the AARRR Pirate Metrics).
Other People’s Networks (OPNs): Leveraging other people’s networks.
OPA: Leveraging other people’s audience (Similar to above).
OPP: Leveraging other people’s platforms. Usually by reverse engineering APIs.
Influence Hacking: Leveraging influence using hacks.
Lean Analytics: Bare minimum tracking, reporting, and analysis.
A/B Testing: Comparing 2 versions to check which performs better, usually by changing one element at a time.
AHA Moment: The time it “clicks”. (Talking about the growth experiments here!)
Churn Rate: Lost customers over time, opposite of retention rate.
CRO: Conversion Rate Optimisation.
Deep Dive: In-depth analysis of any metrics.
Growth Mindset: Growth is about mindset more than skillset and toolset.
Deep Hunting: The process a growth hacker uses to hunt for tools.
Hack: Innovative low-cost high-impact tricks.
Heatmap: This shows how users interact with a website.
Hustle: Working outside your comfort zone in the growth hacking execution phase.
ICE Score: Impact-Confidence-Ease Score. ICE and scored from 1 to 10 and divided by 3. Use the best judgment.
Iterating: The Cycle of “Experiment > Adjust > Experiment”, repeated and analyzed.
Lead Magnet: Bribe potentials to get lead info, sometimes the first step for activation.
Lean: More value from fewer resources.
Leverage: Used as a VERB in growth hacking. As you would’ve noted above.
Lifetime Value (LTV): Overall overtime worth of a client. Used to cap the CPA (Cost Per Acquisition).
Micro Vs Macro Goals: Users usually complete micro goals on your product or site before completing a macro goal.
Sprint: A given period of time when the team works to execute a specific process usually growth experiments typically last 30 days.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP): Using pre-defined processes to save time and resources, essential for growth hackers.
T-Shape: Breadth and Depth of knowledge, growth hackers leverage each other’s core competency to run campaigns as a team.
Traction: Momentum.
With this guide, you have everything you need to become a real growth hacker. Rather than just showing you some fancy and classic examples, I’ve shared the entire process to help you become a true unicorn.
About the Author

RISHABH DEV
“I transform ideas into execution,
experiments into growth machines,
and horses into unicorns.”
My name is Rishabh Dev and I’m the founder at Mapplinks. I have built Mapplinks, a growth marketing consulting and academy, around the growth marketing process I’ve executed for 60+ startups and companies in the past 10 years.
I’m really honored that my growth marketing process is recommended by Entrepreneur, TechInAsia, Hootsuite, Unmetric, Google Business Groups, YourStory and is used in training for teams at Oracle, NUS, TikTok, NUMA, Java, Alcatel, Philips, Accenture, and more.
Learn More: https://mapplinks.com/growth-hacking-book/
Improve Your Growth Marketing Skills
All our content on Growth Marketing is based on 60+ real growth campaigns for startups and businesses.





